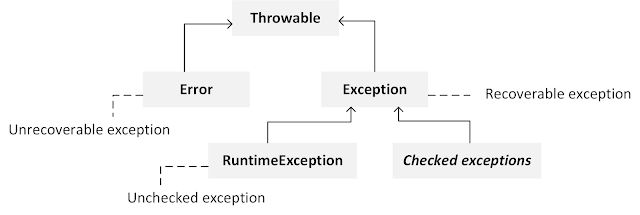
This chapter is taken from the book - Getting started with Java programming language ( https://www.amazon.com/dp/1544614519/ ). You can download the code for the book from here: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B1IwsLB5TOglZXYxWW9JMndUX3M/view Chapter 8 - Exception Handling 8-1 Introduction We saw in chapter 6 that an exception represents a problem with the program that results in immediate termination of the program. In this chapter, we’ll look at: > exceptions that you’ll normally come across while writing Java programs > checked and unchecked exceptions > how to create custom exceptions > how to catch exceptions and handle them gracefully Let’s look at what are exception classes and how they are used in programs. 8-2 Exception classes In Java, an exception is represented by a class. Java defines built-in exception classes representing common exception conditions. For instance, java.lang.Null...
Popular posts from this blog
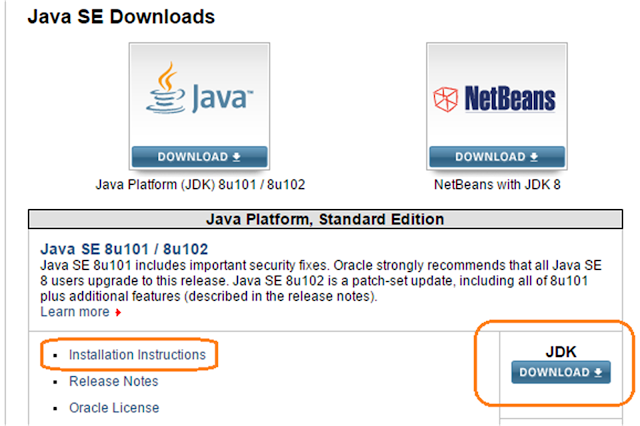
This chapter is taken from the book - Getting started with Java programming language ( https://www.amazon.com/dp/1544614519/ ). You can download the code for the book from here: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B1IwsLB5TOglZXYxWW9JMndUX3M/view Chapter 1 - Hello World! 1-1 Introduction Java is an object-oriented programming language that simplifies writing computer programs. Java was introduced to programmers in 1995 by Sun Microsystems, and is currently maintained by Oracle Corporation. Java programs are platform-independent , that is, the behavior of Java programs remains the same irrespective of the platform (which means the hardware and the operating system) on which you run them. This means that the sample Java programs that accompany this book will behave the same way if you run them on Windows, Ubuntu, Mac, or any other system. In this chapter, we’ll first look at how to download and install the following software that you’ll need for writing and running Java programs...

Comments
Post a Comment